About the disease
What breeds are at risk - Abyssinian, American Curl, American Wirehair, Balinese, Bengal *, Colourpoint Shorthair, Cornish Rex, Javanese,Ocicat, Oriental Shorthair, Siamese, Singapura,Somali, Tonkinese.
* It is possible that Bengals may have the rdAc mutation since Abyssinians were used in the foundation of the breed, but if present this is likely to be at a low prevalence. Recently a specific PRA mutation (PRA-b) was found in the Bengal breed and this mutation likely accounts for the majority of Bengal PRA cases.
Please see the Bengal PRA factsheet for further information.
About the test
At the Molecular Diagnostic Unit, we have developed a PCR-based pyrosequencing assay to quickly and accurately identify the rdAc mutation known to cause PRA in Abyssinian and related breeds.
This assay will allow owners and breeders to identify Affected and Carrier cats and will enable them to inform breeding programs to reduce PRA (rdAc) in their kittens
Interpretation of results
A Normal result on the PRA (rdAc) genetic assay means that the cat does not have the rdAc genetic mutation. It is possible that some cats may go on to develop retinal atrophy due to other, as yet unidentified, genetic mutations.
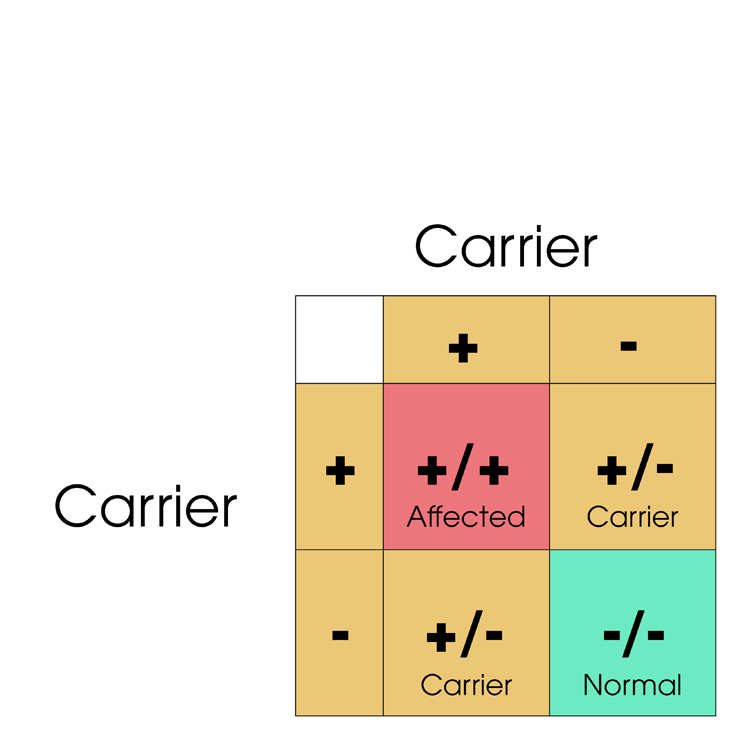
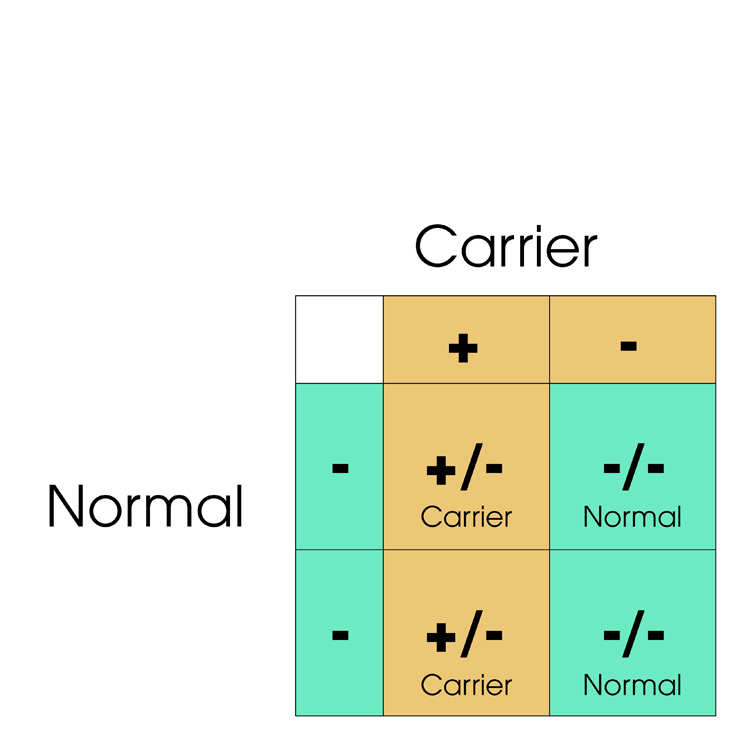
A Carrier result on the PRA (rdAc) genetic assay means that the cat carries one copy of the rdAc genetic mutation. This cat is a Carrier of PRA.
An Affected result on the PRA (rdAc) genetic assay means that the cat carries two copies of the rdAc genetic mutation and will be affected by PRA.
Each certificate we issue will specify whether the cat is Normal, Carrier or Affected for the PRA (rdAc) mutation.
The gene test will help breeders decide whether or not to use cats for breeding. Generally Affected cats should not be used for breeding because they are certain to pass on the genetic mutation. There is a 25% probability of two Carrier cats producing Affected kittens. Breeding Carrier and Normal cats will produce around 50% Normal and 50% Carrier kittens.
This strategy can be used as part of a breeding programme to gradually eliminate the defective gene from the affected populations.
What are the genetics of breeding?
What do I do with a Carrier?
Click here to download -