About the disease
HCM can also be seen in younger cats of specific breeds, including Maine Coons and Ragdolls as a familial disease.
About the test
The Molecular Diagnostic Unit can now offer genetic testing for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in Maine Coon and Ragdoll cats. We have developed PCR-based pyrosequencing assays to quickly and accurately identify the two MYBPC3 gene mutations currently linked with HCM in Maine Coon (A31P) and Ragdoll (R820W) cats.
These mutations cause amino acid changes within the cardiac myosin binding protein and are believed to alter the protein structure and function. It is possible to detect whether a cat has one copy of the defective gene (Heterozygous) or two copies (Homozygous).
There is evidence that the presence of the mutant gene puts cats at greater risk of developing HCM, and the risk for Homozygous cats appears to be greater than that for Heterozygous cats, but this correlation is not perfect. This may be because other, as yet unidentified, genetic mutations can also cause HCM or modify the risk.
There is some evidence that cats Homozygous for the mutant gene are more likely to develop moderate to severe disease earlier in life when compared to Heterozygous cats. Results suggest that the prevalence of the R820W mutation in the Ragdoll population is around 13%.
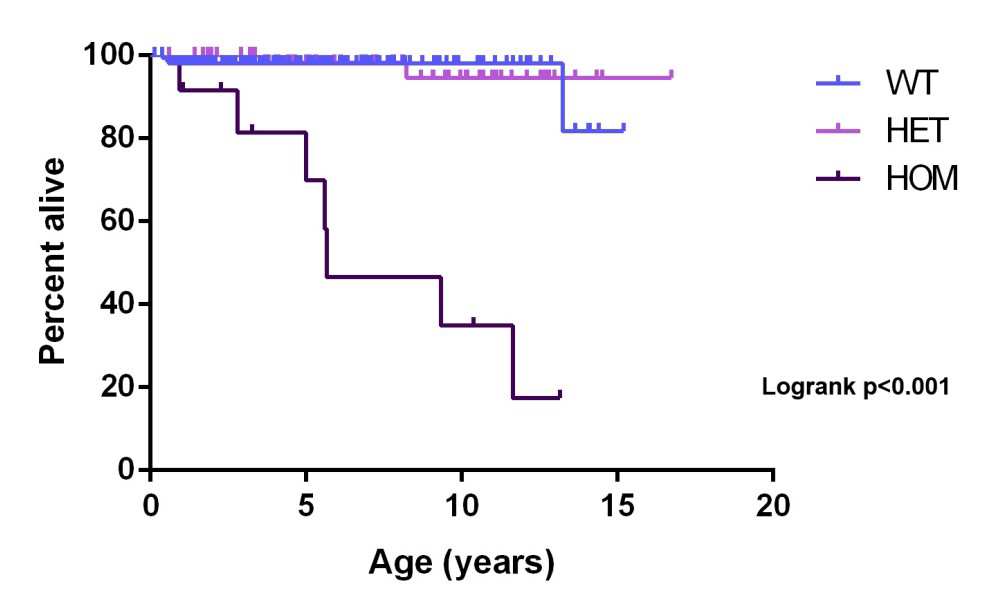
Survival rates for Ragdoll cats with HCM
A recent study undertaken by the Royal Veterinary College and Langford Vets investigated the survival rates of Ragdoll cats with and without the hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutation. The graph below clearly shows that Ragdoll cats Homozygous (HOM) for the mutation have a reduced life expectancy compared to Normal (WT) or Heterozygous (HET) cats. The fact that about 20% of Homozygous cats were still alive at around 12 years of age indicates the incomplete penetrance of this mutation. Over half of the Ragdolls Homozygous for the mutation did not survive 5 years, which shows that genetic testing to identify Heterozygous cats, and
hence avoid breeding Homozygous kittens, is still important for Ragdoll breeders.
Interpretation of results
A Normal result on the Ragdoll HCM genetic test means that the cat does not have the respective genetic mutation. It is possible that some cats may go on to develop cardiac disease due to other, as yet unidentified
genetic mutations.
A Heterozygous or Homozygous result on the Ragdoll HCM genetic test means that the cat carries either one (Heterozygous) or two (Homozygous) mutated copies of the MYBPC3 gene and is at greater risk of developing cardiac disease. Cats that are Homozygous for the genetic mutation are thought likely to develop HCM.
Consideration should be given to screening cats with a positive HCM genetic test result by ultrasound to determine the disease status and progression.
Each certificate we issue will specify whether the cat is Normal, Heterozygous or Homozygous for the Ragdoll HCM mutation.
The gene test combined with ultrasound can assist breeders in deciding whether or not to use cats for breeding. Generally Homozygous affected cats should not be used for breeding because they are certain to pass on the genetic mutation, which will put their offspring at increased risk of developing HCM.
There is a 50% probability of a Heterozygous cat passing on the genetic mutation when bred with a HCM negative cat. In such cases the offspring should be screened for the genetic mutation and those identified as negative used for future breeding. This strategy can be used as part of a breeding programme to eliminate the defective gene from the Maine Coon and Ragdoll populations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can my cat go on the ICC / GCCF negative registers?
Yes, cats that have been tested and are clear of specific genetic diseases can. For cats to be placed on the negative register with organisations such as ICC or GCCF the sample (mouth swab or blood sample) MUST be taken by a vet who confirms the cat’s identity using its microchip number. The microchip number must be written on the submission form AND sample.
We have a dedicated submission form for this purpose, which both the owner and vet must complete. Our result certificate will state that the cat’s identity was confirmed by a vet and you can use this to register the cat on the ICC negative register.
If you DO NOT want your cat to go on these registers then you can take a mouth swab and submit it directly to the lab.
Click here to download -